lambda 表达式的理论基础.md 14 KB
lambda 表达式的理论基础
Java中的 lambda 表达式实质上是一个匿名方法,但该方法并非独立执行,而是用于实现由函数式接口定义的唯一抽象方法。
使用 lambda 表达式时,会创建实现了函数式接口的一个匿名类实例,如 Java8 中的线程 Runnable 类实现了函数接口:@FunctionalInterface。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
平常我们执行一个 Thread 线程:
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("xxxx");
}
}).start();
如果用 lambda 会非常简洁,一行代码搞定。
new Thread(()-> System.out.println("xxx")).start();
所以在某些场景下使用 lambda 表达式真的能减少 java 中一些冗长的代码,增加代码的优雅性。
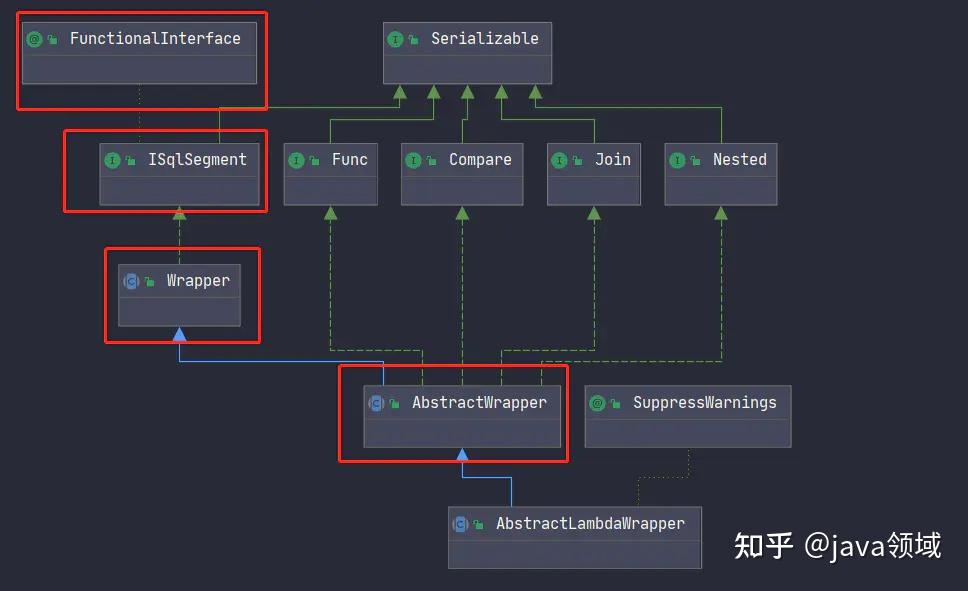
lambda 条件构造器基础类:包装器模式(装饰模式)之 AbstractWrapper AbstractWrapper 条件构造器说明
- 出现的第一个入参 boolean condition 表示该条件是否加入最后生成的 sql 中,例如:query.like(StringUtils.isNotBlank(name), Entity::getName, name) .eq(age!=null && age >= 0, Entity::getAge, age)
- 代码块内的多个方法均为从上往下补全个别 boolean 类型的入参,默认为 true
- 出现的泛型 Param 均为 Wrapper 的子类实例(均具有 AbstractWrapper 的所有方法)
- 方法在入参中出现的 R 为泛型,在普通 wrapper 中是 String ,在 LambdaWrapper 中是函数(例:Entity::getId,Entity 为实体类,getId为字段id的getMethod)
- 方法入参中的 R column 均表示数据库字段,当 R 具体类型为 String 时则为数据库字段名(字段名是数据库关键字的自己用转义符包裹!)!而不是实体类数据字段名!!!,另当 R 具体类型为 SFunction 时项目 runtime 不支持 eclipse 自家的编译器!
- 使用普通 wrapper,入参为 Map 和 List 的均以 json 形式表现!
- 使用中如果入参的 Map 或者 List为空,则不会加入最后生成的 sql 中!
警告:
不支持以及不赞成在 RPC 调用中把 Wrapper 进行传输。
“ Wrapper 很重 传输 Wrapper 可以类比为你的 controller 用 map 接收值(开发一时爽,维护火葬场) 正确的 RPC 调用姿势是写一个 DTO 进行传输,被调用方再根据 DTO 执行相应的操作 我们拒绝接受任何关于 RPC 传输 Wrapper 报错相关的 issue 甚至 pr。
AbstractWrapper 内部结构
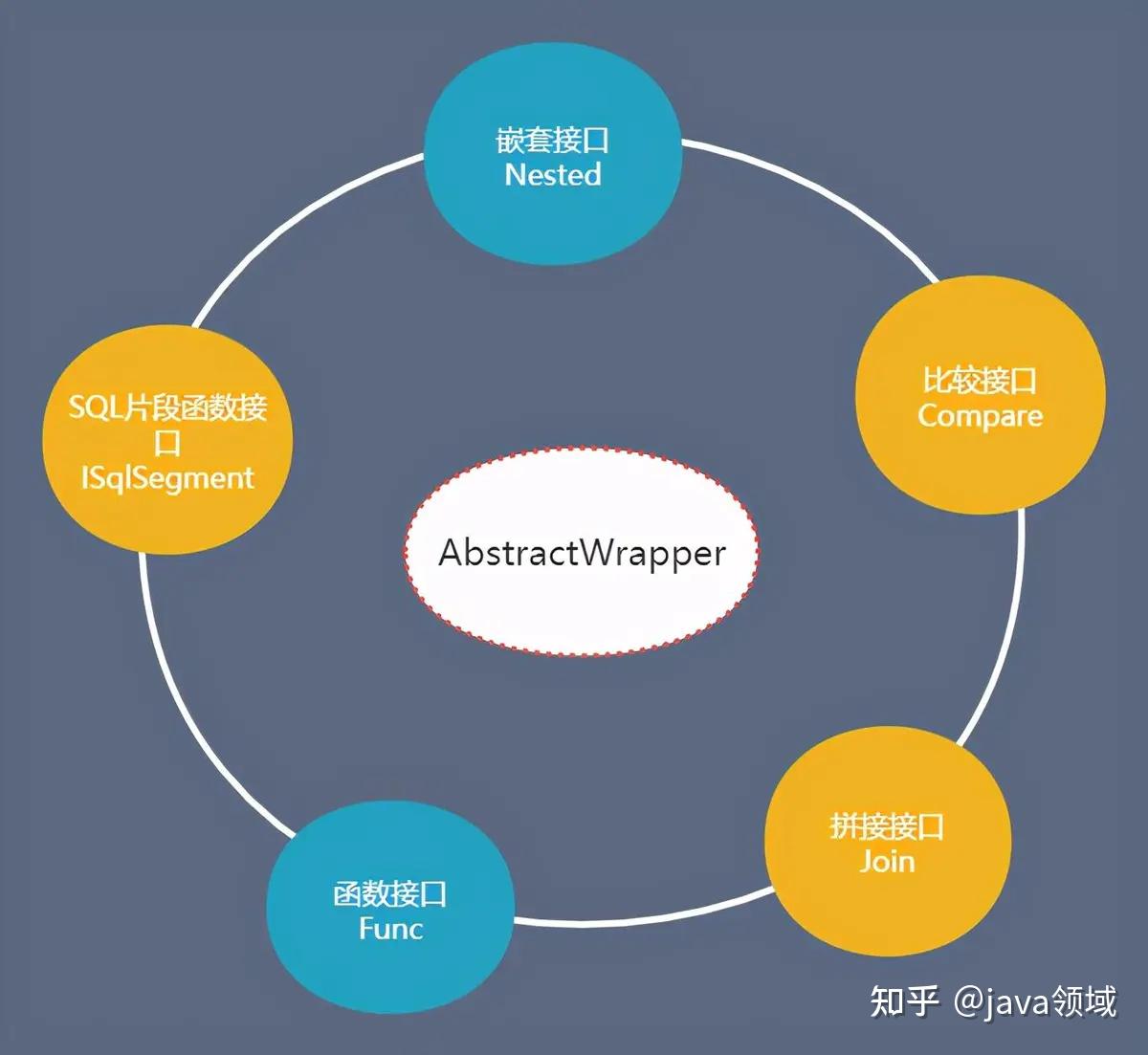
从上图,我们了解到 AbstractWrapper 的实际上实现了五大接口:
- SQL 片段函数接口:ISqlSegment
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ISqlSegment extends Serializable {
/**
* SQL 片段
*/
String getSqlSegment();
}
- 比较值接口 Compare,如 等值 eq、不等于:ne、大于 gt、大于等于:ge、小于 lt、小于等于 le、between、模糊查询:like 等等
- 嵌套接口 Nested ,如 and、or
- 拼接接口 Join,如 or 、exists
- 函数接口 Func,如 in 查询、groupby 分组、having、order by排序等
常用的 where 条件表达式 eq、like、in、ne、gt、ge、lt、le。
@Override
public Children in(boolean condition, R column, Collection<?> coll) {
return doIt(condition, () -> columnToString(column), IN, inExpression(coll));
}
public Children notIn(boolean condition, R column, Collection<?> coll)
public Children inSql(boolean condition, R column, String inValue)
public Children notInSql(boolean condition, R column, String inValue)
public Children groupBy(boolean condition, R... columns)
public Children orderBy(boolean condition, boolean isAsc, R... columns)
public Children eq(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
public Children ne(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
public Children gt(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
public Children ge(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
public Children lt(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
public Children le(boolean condition, R column, Object val)
...
/**
* 普通查询条件
*
* @param condition 是否执行
* @param column 属性
* @param sqlKeyword SQL 关键词
* @param val 条件值
*/
protected Children addCondition(boolean condition, R column, SqlKeyword sqlKeyword, Object val) {
return doIt(condition, () -> columnToString(column), sqlKeyword, () -> formatSql("{0}", val));
}
SQL 片段函数接口
lambda 这么好用的秘诀在于 SQL 片段函数接口:ISqlSegment,我们在 doIt 方法找到 ISqlSegment 对象参数,翻开 ISqlSegment 源码,发现它真实的庐山真面目,原来是基于 Java 8 的函数接口 @FunctionalInterface 实现!
ISqlSegment 就是对 where 中的每个条件片段进行组装。
/**
* 对sql片段进行组装
*
* @param condition 是否执行
* @param sqlSegments sql片段数组
* @return children
*/
protected Children doIt(boolean condition, ISqlSegment... sqlSegments) {
if (condition) {
expression.add(sqlSegments);
}
return typedThis;
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ISqlSegment extends Serializable {
/**
* SQL 片段
*/
String getSqlSegment();
}
从 MergeSegments 类中,我们找到 getSqlSegment 方法,其中代码片段
sqlSegment = normal.getSqlSegment() + groupBy.getSqlSegment() + having.getSqlSegment() + orderBy.getSqlSegment()
这段代码表明,一条完整的 where 条件 SQL 语句,最终由 normal SQL 片段,groupBy SQL 片段,having SQL 片段,orderBy SQL 片段拼接而成。
@Getter
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class MergeSegments implements ISqlSegment {
private final NormalSegmentList normal = new NormalSegmentList();
private final GroupBySegmentList groupBy = new GroupBySegmentList();
private final HavingSegmentList having = new HavingSegmentList();
private final OrderBySegmentList orderBy = new OrderBySegmentList();
@Getter(AccessLevel.NONE)
private String sqlSegment = StringPool.EMPTY;
@Getter(AccessLevel.NONE)
private boolean cacheSqlSegment = true;
public void add(ISqlSegment... iSqlSegments) {
List<ISqlSegment> list = Arrays.asList(iSqlSegments);
ISqlSegment firstSqlSegment = list.get(0);
if (MatchSegment.ORDER_BY.match(firstSqlSegment)) {
orderBy.addAll(list);
} else if (MatchSegment.GROUP_BY.match(firstSqlSegment)) {
groupBy.addAll(list);
} else if (MatchSegment.HAVING.match(firstSqlSegment)) {
having.addAll(list);
} else {
normal.addAll(list);
}
cacheSqlSegment = false;
}
@Override
public String getSqlSegment() {
if (cacheSqlSegment) {
return sqlSegment;
}
cacheSqlSegment = true;
if (normal.isEmpty()) {
if (!groupBy.isEmpty() || !orderBy.isEmpty()) {
sqlSegment = groupBy.getSqlSegment() + having.getSqlSegment() + orderBy.getSqlSegment();
}
} else {
sqlSegment = normal.getSqlSegment() + groupBy.getSqlSegment() + having.getSqlSegment() + orderBy.getSqlSegment();
}
return sqlSegment;
}
}
lambda 构建复杂的查询条件构造器:LambdaQueryWrapper
LambdaQueryWrapper 四种不同的 lambda 构造方法
- 方式一 使用 QueryWrapper 的成员方法方法 lambda 构建 LambdaQueryWrapper
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lambda = new QueryWrapper<UserEntity>().lambda();
- 方式二 直接 new 出 LambdaQueryWrapper
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lambda = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
- 方式三 使用 Wrappers 的静态方法 lambdaQuery 构建 LambdaQueryWrapper 推荐
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lambda = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
- 方式四:链式查询
List<UserEntity> users = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<UserEntity>(userMapper)
.like(User::getName, "雨").ge(User::getAge, 20).list();
笔者推荐使用 Wrappers 的静态方法 lambdaQuery 构建 LambdaQueryWrapper 条件构造器。
1 等值查询:eq
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfEq() {
//eq查询
//相当于 select * from sys_user where user_id = 1
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(UserEntity::getUserId, 1L);
UserEntity user = userMapper.selectOne(lqw);
System.out.println("eq查询::" + user.getUserName());
}
eq 查询等价于原生 sql 的等值查询。
select * from sys_user where user_id = 1
2 范围查询 :in
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfIn() {
List<Long> ids = Arrays.asList(1L, 2L);
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.in(UserEntity::getUserId, ids);
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("in查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
in 查询等价于原生 sql 的 in 查询
select * from sys_user where user_id in (1,2)
3 通配符模糊查询:like
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfLikeAll() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(UserEntity::getSex, 0L)
.like(UserEntity::getUserName, "dun");
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("like全包含关键字查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
like 查询等价于原生 sql 的 like 全通配符模糊查询。
select * from sys_user where sex = 0 and user_name like '%dun%'
4 右通配符模糊查询:likeRight
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfLikeRight() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(UserEntity::getSex, 0L)
.likeRight(UserEntity::getUserName, "dun");
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("like Right含关键字查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
likeRight 查询相当于原生 sql 的 like 右通配符模糊查询。
select * from sys_user where sex = 0 and user_name like 'dun%'
5 左通配符模糊查询:likeLeft
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfLikeLeft() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(UserEntity::getSex, 0L)
.likeLeft(UserEntity::getUserName, "zung");
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("like Left含关键字查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
likeLeft 查询相当于原生 sql 的 like 左通配符模糊查询。
select * from sys_user where sex = 0 and user_name like '%zung'
6 条件判断查询
条件判断查询类似于 Mybatis 的 if 标签,第一个入参 boolean condition 表示该条件是否加入最后生成的 sql 中。
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfBoolCondition() {
UserEntity condition = UserEntity.builder()
.sex(1)
.build();
//eq 或 like 条件判断查询
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(condition.getSex() != null, UserEntity::getSex, 0L)
// 满足 bool 判断,是否进查询按字段 userName 查询
.like(condition.getUserName() != null, UserEntity::getUserName, "dun");
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("like查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
7 利用 or 和 and 构建复杂的查询条件
@Test
public void testLambdaQueryOfOr_And() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.eq(UserEntity::getSex, 0L)
.and(wrapper->wrapper.eq(UserEntity::getUserName,"dunzung")
.or().ge(UserEntity::getAge, 50));
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("like查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
上面实例查询等价于原生 sql 查询:
select * from sys_user where sex = 0 and (use_name = 'dunzung' or age >=50)
8 善于利用分页利器 PageHelpler
@Test
public void testLambdaPage() {
//PageHelper分页查询
//相当于 select * from sys_user limit 0,2
int pageNumber = 0;
int pageSize = 2;
PageHelper.startPage(pageNumber + 1, pageSize);
LambdaQueryWrapper<UserEntity> lqw = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
lqw.orderByAsc(UserEntity::getAge)
.orderByDesc(UserEntity::getMobile);
List<UserEntity> userList = userMapper.selectList(lqw);
userList.forEach(u -> System.out.println("page分页查询::" + u.getUserName()));
}
上面实例查询等价于原生 sql 分页查询:
select * from sys_user order by age desc,mobile desc limit 0,2
另外,Mybatis-Plus 自带分页组件,BaseMapper 接口提供两种分页方法来实现物理分页。
- 第一个返回实体对象允许 null
- 第二个人返回 map 对象多用于在指定放回字段时使用,避免为指定字段 null 值出现
IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(IPage<T> page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
注意,Mybatis-Plus 自带分页组件时,需要配置 PaginationInterceptor 分页插件。
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
9 更新条件构造器:LambdaUpdateWrapper
@Test
public void testLambdaUpdate() {
LambdaUpdateWrapper<UserEntity> luw = Wrappers.lambdaUpdate();
luw.set(UserEntity::getUserName, "dunzung01")
.set(UserEntity::getSex, 1);
luw.eq(UserEntity::getUserId, 1);
userMapper.update(null, luw);
}